While many IT professionals see data management and security as separate functions, there has been, and will continue to be an overlap in responsibilities. And new challenges facing organizations will only drive those dependencies deeper.
Unbeknownst to many data management professionals, their programs for backup and recovery, disaster recovery, and business continuity are prescribed by the leading security frameworks and principles. Let’s take a quick tour of a few of the security principles, frameworks, and privacy laws that illustrate this point.
A Closer Look at the Leading Security Frameworks and Principles
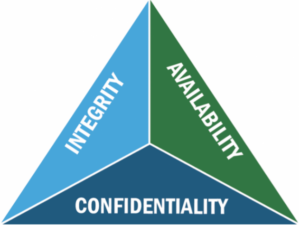
The CIA Triad
CIA Triad (Source Department of Energy.com)
The CIA Triad provides a model for the broad security categories of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It provides the guiding principles of an effective information security program. And data management professionals have a clear role for the availability function of the CIA Triad.
- Confidentiality and integrity fall into classic security regarding access controls, encryption, role-based access control (RBAC), etc.
- Availability is defined as: Authorized users should be able to access data whenever they need to do so.
- The need here is clear for data management with backup and recovery delivering disaster recovery and business continuity to ensure data access is provided whenever needed.
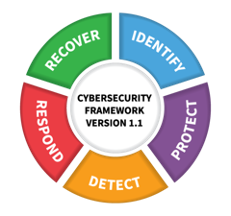
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is typically seen as the domain of security practitioners; it has five functional areas: identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover.
- The recover functionality is supported by data management with backup and recovery, enabling the organization to return to operations after a disaster, system failure, or cyberattack.
- Recover (as defined by NIST) says: “Develop and implement appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. The Recover Function supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact from a cybersecurity incident.”
GDPR
GDPR is commonly understood as a regulation for ensuring the data privacy of EU citizens, but it has specific language for the availability and accessibility of personal data.
- Article 32 – Security of processing
- 1. C. the ability to restore the availability and access to personal data in a timely manner in the event of a physical or technical incident.
- Data management professionals need to ensure that backup and recovery provides the ability to recover in a “timely manner”; while this is vague, GDPR does specify that organizations must respond to data subject access requests (DSARs) within 30 calendar days. Any availability problems could potentially interfere with the timely response and lead to violations.
HIPAA
As with GDPR, many IT professionals view HIPAA as the protection of health information.
- But HIPAA also provides specific language for data management, in terms of backup and recovery, as part of “§ 164.308 Administrative safeguards”:
- (ii) Implementation specifications:
- (A) Data backup plan (required). Establish and implement procedures to create and maintain retrievable exact copies of electronic protected health information.
- (B) Disaster recovery plan (required). Establish (and implement as needed) procedures to restore any loss of data.
- (ii) Implementation specifications:
The Modern CISO
The role of the chief information security officer (CISO) emerged in the mid 90s with the introduction of the Internet. The role has continually progressed and includes oversight on many critical security and operational issues, including business continuity and disaster recovery.
A quick tour of LinkedIn job postings illustrates the oversight the CISO has for disaster recovery and business continuity, further emphasizing the role of data management in security. Here are requirements from selected CISO job postings:
- Retail CISO: Ensure business continuity and disaster recovery procedures are consistently up-to-date and well tested to minimize risk to the organization.
- Aerospace CISO: Develops and oversees effective disaster recovery policies and standards.
- Healthcare CISO: Review and ensure organization’s Business Continuity Plan meets requirements of regulatory agencies.
DAMA International
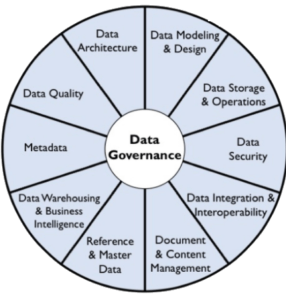
DAMA International is dedicated to advancing the concepts and practices of information and data management and supporting DAMA members and their organizations to address their information and data management needs.
With DAMA, we have an example of data security being required in data management rather than data management as a part of security in the previous examples.
- DAMA’s data management body of knowledge (DMBOK) defines (11) knowledge areas of data management, tied together by data governance which includes data security.
- Data Security – ensuring privacy, confidentiality, and appropriate access to PII, PHI, and an individual’s private data
- From DAMA’s perspective, data security is a key responsibility of data management, although it is a shared responsibility between data and security teams.
From the brief overviews above, data management, in the form of backup and recovery, is an integral part of the CIA Triad, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, GDPR, HIPAA, and CISO responsibilities. And from the data management perspective, data security is one of the (11) DMBOK knowledge areas for data management.
These issues have been driving increasing collaboration of data management and security for many years. But two factors have dramatically accelerated this trend: ransomware and mass data fragmentation.
Ransomware and Mass Data Fragmentation Drive Security and Data Management Collaboration
Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are prolific and fill today’s headlines. Organizations must be prepared for the inevitable strike against their organization. Research has indicated that ransomware attacks have increased up to 500% in the last year and show no signs of waning. Ransomware has become institutionalized with cybercrime organizations specializing in delivering various services and tools to support ransomware attacks.
Here we have one of the clearest and most urgent needs for tight collaboration between data management and security. Now, backup data is actively targeted by hackers so that they can hold organizations hostage to their monetary demands. The sophistication of attacks raises the bar on backup and recovery, and security becomes essential to ensuring the availability and integrity of backup copies. Having secure backups and the ability to rapidly recover is perhaps the strongest countermeasure to ransomware.
Security teams need to collaborate with data management teams to ensure that backup and recovery are hardened to thwart the destructive effect of ransomware on business operations:
- There are no backdoors for support or administrative staff to modify or delete backup copies or backup schedules.
- Multiple people are required to approve changes to backup schedules or to delete copies, and access is controlled via multifactor authentication (MFA) and RBAC.
- Backup data is immutable and is supported with fault tolerance.
- Instant mass recovery is supported.
- There are anomaly detection alerts of potential ransomware activity.
- Security teams can use global search and forensics to support remediation and post-event forensic analysis.
Mass Data Fragmentation
Mass data fragmentation describes the growing proliferation of data spread across a myriad of different locations, infrastructure silos, and management systems that prevents organizations from fully utilizing its value. Further, organizations will struggle to protect and secure this fragmented data.
There are several issues that data management and security face with mass data fragmentation:
- Location: Where is the organization’s data? The challenge is understanding the physical and logical locations given cloud, SaaS, IaaS, and edge computing.
- Classification: What type of data is stored at various locations and how critical is that information to operations, security, and compliance?
- Usage: Who is using the data? Is their use of the data appropriate for their role and responsibilities?
- Protection: Is the data protected and secured?
In dealing with mass data fragmentation, data management will again support the security function with data governance, providing the data intelligence necessary to ensure that security architecture and controls are appropriate for the fragmented data. And of course, this data intelligence will help data management teams apply the appropriate protection to this fragmented data for backups, supporting disaster recovery and business continuity, and to thwart ransomware attacks.
Data Management Is Integral to Cybersecurity and Data Security Is Integral to Data Management
Data management has an important role in fulfilling the principles, frameworks, and regulations of information security and privacy. Similarly, security is key for the data management function. As our information technology continues to grow more diverse and threats become more acute, this interdependency will only grow. Each function brings its unique perspective and skills to ensure that the organization can leverage data for optimal and efficient operations. This collaboration of data management and information security is foundational to defeating ransomware and other cybersecurity threats.